Reproductive System
Genital Tract Embryology
| Primordial | Female | Male |
|---|---|---|
| Gubernaculum | Ovarian ligament Round ligament | - |
| Processus vaginalis | - | Tunica vaginalis |
| Undifferentiated gonads | Ovary | Testis |
| Theca cell | Leydig cell | |
| Granulosa cell | Sertoli cell | |
| Genital ducts | Frimbriae | Epididymis |
| Fallopian tube | Vas deferens | |
| Uterus | Seminal vesicle | |
| Upper vagina | Ejaculatory duct | |
| Urogenital sinus | Lower vagina | Prostatic utricle |
| Paraurethral gland of Skene | Prostate gland | |
| Greater vestibular gland of Bartholin | Bulbourethral gland of Cowper | |
| Urogenital fold | Mons pubis | Dorsal penile shaft |
| Labia minora | Ventral penile shaft | |
| Labioscrotal swelling | Labia majora | Scrotum |
| Genital tubercle | Clitoris | Penis |
Ligaments of Uterus and Ovary
| Ligament | Connects | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Broad ligament | Uterus ~ Pelvis :: lateral | - |
| Round ligament | Uterus ~ Labia majora | Gubernaculum |
| Ovarian ligament | Uterus ~ Ovary | Gubernaculum |
| Infundibulopelvic [Suspensory] ligament | Ovary ~ Pelvis :: lateral | Ovarian vessels |
| Pubocervical ligament | Cervix ~ Pubis | - |
| Cardinal ligament | Cervix ~ Pelvis :: lateral | Uterine vessels |
| Uterosacral ligament | Cervix ~ Sacrum | Inferior hypogastric plexus |

Sex Hormone Production
| Hormones | Regulation | Female | Male |
|---|---|---|---|
| Progesterone DHEA Androstenedione Testosterone | ACTH | Adrenal gland | Adrenal gland |
| Progesterone Testosterone | LH | Corpus luteum Theca cells | Leydig cells |
| Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) Estradiol Inhibin | FSH | Corpus luteum Granulosa cells | Sertoli cells |
| Estrone | - | Adipocytes | Adipocytes |
| Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) | - | Peripheral cells | Peripheral cells |
Estrogens in Females
| Estrogen | Estrogen Site | Precursor | Precursor Site | Enzyme | Timing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estrone | Adipocytes | Androstenedione | Adrenal gland | Aromatase | Post-menopause |
| Estradiol | Granulosa cells | Testosterone | Theca cells | Aromatase | Non-pregnancy |
| Estriol | Placenta | DHEA sulfate (DHEAS) | Adrenal gland | Sulfatase | Pregnancy |
Etiology of Incresed Exposure to Estrogen
- Nulliparity
- Early menarche
- Late menopause
Side Effects of Unopposed Estrogen
- ↑ Thromboembolism
- ↑ Breast cancer
- ↑ Endometrial cancer
- ↑ Bone mineral density
Sexual Development
| Female | Male |
|---|---|
| Thelarche | Gonadarche |
| Pubarche | Pubarche |
| Growth spurt | Adrenarche |
| Menarche | Growth spurt |
Age of Onset of Puberty
| Sex | Age (years) |
|---|---|
| Female | 8 ~ 13 |
| Male | 9 ~ 14 |
Etiology of Peripheral Precocious Puberty
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Adrenal tumors
- Gonadal tumors
- McCune-Albright syndrome
- Exogenous sex hormone
Etiology of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB) {PALM-COEIN}
- Pregnancy
- Polyps
- Adenomyosis
- Leiomyoma
- Malignancy
- Coagulopathy
- Ovulatory dysfunction
- Endometrium
- Iatrogenic
- Not yet classified
Classification of Amenorrhea
- Primary: no menarche by age 15 years
- Secondary: no menses for ≥ 3 cycles / ≥ 6 months
Etiology of Primary Amenorrhea
| Etiology | Breast | Uterus | Ovary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outflow obstruction | + | + | + |
| Anorexia nervosa | + | + | + |
| Mullerian agenesis | + | - | + |
| Androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) | + | - | - |
| Constitutional growth delay | - | + | + |
| Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism | - | + | + |
| Turner syndrome | - | + | + |
| Swyer syndrome | - | + | - |
Etiology of Secondary Amenorrhea
| Etiology | GnRH | LH & FSH | SH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pregnancy | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Menopause [Ovarian failure] | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ |
| Resistant ovary [Savage] syndrome | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ |
| Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) | ↑/↓ | ↑/↓ | ↓/↑ |
| Asherman syndrome | - | - | - |
| Outflow obstruction | - | - | - |
Presentation of Turner Syndrome
- Streak gonads
- Amenorrhea
- Webbed neck
- Shield chest
- Bicuspid aortic valve
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Cystic hygroma
Indicators of Ovarian Reserve
| Indicator | Normal |
|---|---|
| FSH :: follicular phase | 2 ~ 8 |
| Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) | 1 ~ 5 |
| Antral follicle count (AFC) | 5 ~ 10 |
Presentation of Menopause {HAVOCS}
- Hot flashes
- Atrophy of the vagina
- Osteoporosis
- Cardiovascular disease
- Sleep disturbances
Treatment of Menopause
- Topical estrogen
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- SSRIs & SNRIs
- Calcium & Vitamin D supplements
Side Effects of Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
- ↑ Thromboembolism
- Breast cancer
- ↑ if estrogen + progesterone
- ↓ if estrogen alone
- Endometrial cancer
- ↓ if estrogen + progesterone
- ↑ if estrogen alone
- ↓ Fractures
Hormones Changes in PCOS
| Hormone | Changes |
|---|---|
| GnRH | ↑/↓ |
| LH | ↑ |
| FSH | ↓ |
| LH/FSH | ↑ |
| Progesterone | ↓ |
| Testosterone | ↑ |
| Estrogen | ↑ |
Rotterdam Criteria for Diagnosis of PCOS
- Anovulation
- Hyperandrogenism
- Polycystic ovaries
Treatment of PCOS
- Ovulation induction
- Estrogen modulators :: Clomiphene
- Aromatase inhibitors
- Combined hormonal contraception
- Androgen antagonists
- 5α-Reductase inhibitors
- Metformin ± Statins
- Lifestyle modification
Non-surgical Treatment of Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP)
- Kegel exercise
- Topical estrogen
- Pessary
Pathogens of Genital Tract Infection
| Pathogen | Presentation | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | Discharge :: greenish-yellow Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) | 3° Cephalosporins Macrolides |
| Haemophilus ducreyi | Painful chancroid | - |
| Klebsiella granulomatis | Granuloma inguinale | Macrolides Doxycycline |
| Treponema pallidum | Painless chancre Condyloma lata | Penicillin |
| Chlamydia trachomatis | Discharge :: greenish-yellow Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) | Macrolides Doxycycline |
| Gardnerella vaginalis | Discharge :: grayish & fishy | Metronidazole |
| Candida albicans | Discharge :: white & curdy | -Conazoles |
| Trichomonas vaginalis | Discharge :: greenish-yellow & frothy | Metronidazole |
| HPV | Condyloma accumulata Verruca vulgaris | - |
| HSV | Paniful ulcers | - |
Comparison Between Testicular Torsion and Epididymitis
| Testicular Torsion | Epididymitis | |
|---|---|---|
| Prehn sign | - | + |
| Cremasteric reflex | - | + |
| Blood flow | ↓ | ↑ |
Medications for BPH
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| α1 antagonists | Tamsulosin Terazosin Doxazosin Prazosin |
| 5α-Reductase inhibitors | Finasteride |
Reproductive Tumors
Epithelial Tumors
- Serous cystadenoma
cystadenocarcinoma - Mucinous cystadenoma
cystadenocarcinoma - Endometrioid carcinoma
- Clear cell carcinoma
- Mixed cell carcinoma
- Transitional cell carcinoma [Brenner tumor]
- Carcinosarcoma [Malignant mixed Mullerian tumor (MMMT)]
Stromal Tumors
| Female | Male | Markers |
|---|---|---|
| Theca cell tumor [Thecoma] | Leydig cell tumor | - |
| Granulosa cell tumor | Sertoli cell tumor | Inhibin |
| Fibroma | Fibroma | - |
Germ Cell Tumors (GCT)
| Female | Male | Markers |
|---|---|---|
| Dysgerminoma | Seminoma | ALP & LDH |
| Choriocarcinoma | Choriocarcinoma | hCG |
| Endodermal sinus tumor (EST) | Endodermal sinus tumor (EST) | AFP |
| Embryonal carcinoma | Embryonal carcinoma | hCG & AFP |
| Teratoma | Teratoma | hCG & AFP |
Triad of Meigs Syndrome
- Ovarian fibroma
- Pleural effusion
- Ascites
Types of Endometrial Cancer
| Type | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Histology | Endometrioid | Non-endometrioid |
| Risk factors | Estrogen | - |
| Prognosis | Favorable | Poor |
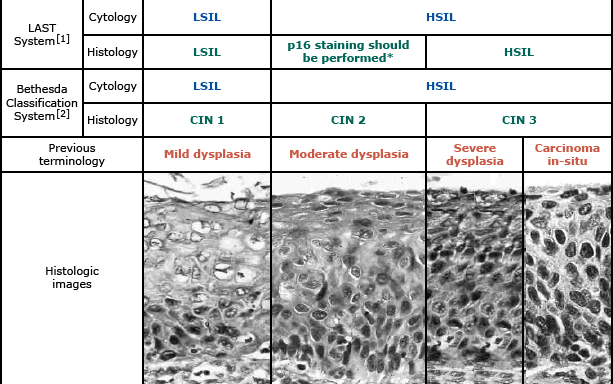
Bethesda System for Pap Smear Results
- Squamous cell abnormalities
- Atypical squamous cell (ASC)
- Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL)
- High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL)
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Glandular cell abnormalities
- Atypical glandular cell (AGC)
- Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS)
- Adenocarcinoma
Management of Abnormal Pap Smear Results
| Result | Age (years) | HPV | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | < 30 | ±/? | Routine screening |
| - | > 30 | -/? | Routine screening |
| - | > 30 | + | Repeat screening in 1 year |
| ASC-US | < 25 | - | Routine screening |
| ASC-US | < 25 | +/? | Repeat screening in 1 year |
| ASC-US | > 25 | - | Repeat screening in 3 years |
| ASC-US | > 25 | ? | Repeat screening in 1 year |
| LSIL | < 25 | ±/? | Repeat screening in 1 year |
| LSIL | > 25 | - | Repeat screening in 1 year |
| Consecutive Otherwise | Any | ±/? | Colposcopy ± Biopsy |
Management of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN)
| CIN | Management |
|---|---|
| I | Repeat screening in 1 year |
| II III | Cryotherapy Laser ablation Conization Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) |
Management of Seminoma
- Radical orchiectomy
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Contraception Methods
- Barrier contraception
- Combined hormonal contraception
- Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs)
- Contraceptive patch
- contraceptive ring
- Depot medroxyprogesterone
- Progestin subdermal implant
- Intrauterine devices
- Progestin intrauterine device
- Copper intrauterine device
Side Effects of Combined Hormonal Contraception
- ↑ Thromboembolism
- ↑ Breast cancer
- ↓ Endometrial cancer
- ↓ Ovarian cancer
Contraindications to Combined Hormonal Contraception
- Age ≥ 35 years
Smoking ≥ 15 cigarettes/day - History of thromboembolism
- Active breast cancer
- Liver failure
- Migraines with aura
Contraindications to Intrauterine Device (IUD)
- Pregnancy
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding
- Endometrial cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Reference Limits of Semen Analysis
- Volume > 1.5 mL
- Sperm concentration > 15 M/mL
- Total sperm count > 39 M
- Normal forms > 4%
- Vitality > 58%
- Progressive motility > 32%
- Total motility > 40%
Indications for Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
- Cervical factors
- Male factors
- Donor sperms
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
- Tubal factors
- Donor eggs
- Genetic screening
- Failed intrauterine insemination (IUI)
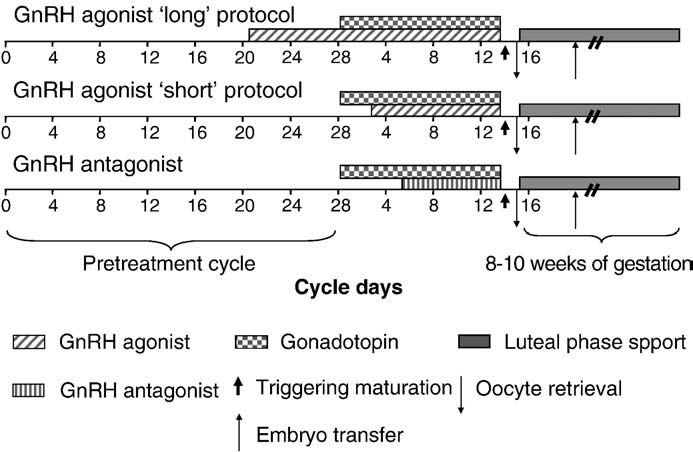
Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation
Suppression of Spontaneous Ovulation
| Protocol | Timing |
|---|---|
| GnRH agonist long protocol | Last luteal phase |
| GnRH agonist short protocol | Menstruation |
| GnRH antagonist protocol | Leading follicle > 14 mm |
Ovulation Induction
- (Follicles > 18 mm) ≥ 2
- Estradiol per co-dominant follicle > 200 pg/mL
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| GnRH agonists | Leuprolide |
| hCG agonists | Choriogonadotropin |
Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)
| Category | Interpretation | Management | Likelihood of cancer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Inconclusive | Repeat | - |
| 1 | Negative | Routine | 0 |
| 2 | Benign | Routine | 0 |
| 3 | Probably benign | Every 6 months | < 2% |
| 4 | Suspicious | Biopsy | 2 ~ 95% |
| 5 | Highly suggestive | Biopsy | > 95% |
| 6 | Biopsy-proven | - | - |
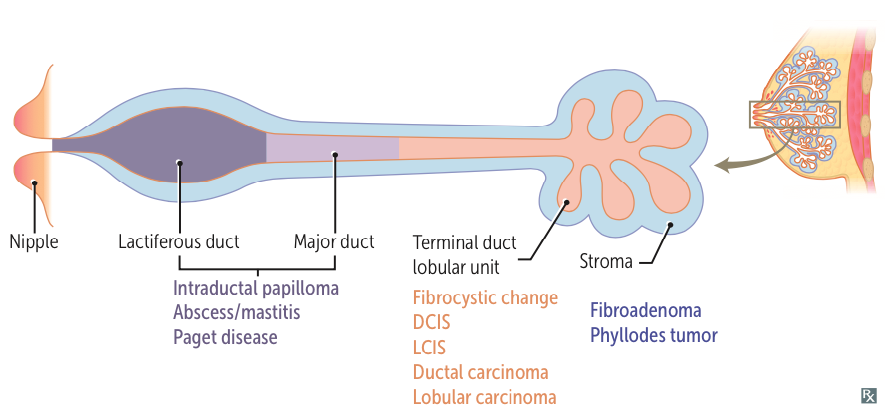
Breast Tumors
Epithelial Tumors
- Fibrocystic change
- Intraductal papilloma
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) - Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) - Medullary carcinoma
Stromal Tumors
- Fibroadenoma
- Phyllodes tumor
Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer
| Subtype | Receptors | Mutations |
|---|---|---|
| Luminal A | PR & ER | - |
| Luminal B | PR & ER | - |
| HER2-enriched | HER2 | - |
| Basal-like | - | BRCA |
| Claudin-low | - | BRCA |
| Interferon-rich | - | BRCA |

Types of Flaps for Breast Reconstruction
- Transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap
- Latissimus dorsi (LD) flap
- Deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flap
- Superficial inferior epigastric artery (SIEA) flap
- Gluteal flap
- Transverse upper gracilis (TUG) flap
- Profunda artery perforator (PAP) flap